Scientists working with data from the Sloan Digital Sky Surveys’ Apache Point Observatory Galactic Evolution Experiment (APOGEE) have discovered a “fossil galaxy” hidden in the depths of our own Milky Way.
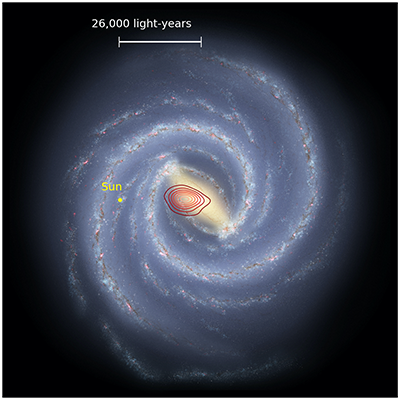
An artist’s impression of what the Milky Way might look like seen from above. The colored rings show the rough extent of the fossil galaxy known as Heracles. The yellow dot shows the position of the Sun.
Image credit: Danny Horta-Darrington (Liverpool John Moores University), NASA/JPL-Caltech, and the SDSS
This result, published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, may shake up our understanding of how the Milky Way grew into the galaxy we see today.
The proposed fossil galaxy may have collided with the Milky Way ten billion years ago, when our galaxy was still in its infancy. Astronomers named it Heracles, after the ancient Greek hero who received the gift of immortality when the Milky Way was created.
The remnants of Heracles account for about one third of the Milky Way’s spherical halo. But if stars and gas from Heracles make up such a large percentage of the galactic halo, why didn’t we see it before? The answer lies in its location deep inside the Milky Way.
“To find a fossil galaxy like this one, we had to look at the detailed chemical makeup and motions of tens of thousands of stars,” says Ricardo Schiavon from Liverpool John Moores University (LJMU) in the UK, a key member of the research team. “That is especially hard to do for stars in the center of the Milky Way, because they are hidden from view by clouds of interstellar dust. APOGEE lets us pierce through that dust and see deeper into the heart of the Milky Way than ever before.”
Ricardo Schiavon
“APOGEE lets us pierce through that dust and see deeper into the heart of the Milky Way than ever before.”
APOGEE does this by taking spectra of stars in near-infrared light, instead of visible light, which gets obscured by dust. Over its ten-year observational life, APOGEE has measured spectra for more than half a million stars all across the Milky Way, including its previously dust-obscured core.
Graduate student Danny Horta from LJMU, the lead author of the paper announcing the result, explains, “examining such a large number of stars is necessary to find unusual stars in the densely-populated heart of the Milky Way, which is like finding needles in a haystack.”
To separate stars belonging to Heracles from those of the original Milky Way, the team made use of both chemical compositions and velocities of stars measured by the APOGEE instrument.
An all-sky image of the stars in the Milky Way as seen from Earth. The colored rings show the approximate extent of the stars that came from the fossil galaxy known as Heracles. The small objects to the lower right of the image are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, two small satellite galaxies of the Milky Way.
Image credit: Danny Horta-Darrington (Liverpool John Moores University), ESA/Gaia, and the SDSS
“Of the tens of thousands of stars we looked at, a few hundred had strikingly different chemical compositions and velocities,” Horta said. “These stars are so different that they could only have come from another galaxy. By studying them in detail, we could trace out the precise location and history of this fossil galaxy.”
Because galaxies are built through mergers of smaller galaxies across time, the remnants of older galaxies are often spotted in the outer halo of the Milky Way, a huge but very sparse cloud of stars enveloping the main galaxy. But since our Galaxy built up from the inside out, finding the earliest mergers requires looking at the most central parts of the Milky Way’s halo, which are buried deep within the disc and bulge.
Stars originally belonging to Heracles account for roughly one third of the mass of the entire Milky Way halo today – meaning that this newly-discovered ancient collision must have been a major event in the history of our Galaxy. That suggests that our Galaxy may be unusual, since most similar massive spiral galaxies had much calmer early lives.
“As our cosmic home, the Milky Way is already special to us, but this ancient galaxy buried within makes it even more special,” Schiavon says.
Karen Masters, the Spokesperson for SDSS-IV comments, “APOGEE is one of the flagship surveys of the fourth phase of SDSS, and this result is an example of the amazing science that anyone can do, now that we have almost completed our ten-year mission.”
And this new age of discovery will not end with the completion of APOGEE observations. The fifth phase of the SDSS has already begun taking data, and its “Milky Way Mapper” will build on the success of APOGEE to measure spectra for ten times as many stars in all parts of the Milky Way, using near-infrared light, visible light, and sometimes both.
Images
Image #1
An artist’s impression of what the Milky Way might look like seen from above. The colored rings show the rough extent of the fossil galaxy known as Heracles. The yellow dot shows the position of the Sun.
Image credit: Danny Horta-Darrington (Liverpool John Moores University), NASA/JPL-Caltech, and the SDSS
Image #2
An all-sky image of the stars in the Milky Way as seen from Earth. The colored rings show the approximate extent of the stars that came from the fossil galaxy known as Heracles. The small objects to the lower right of the image are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, two small satellite galaxies of the Milky Way.
Image credit: Danny Horta-Darrington (Liverpool John Moores University), ESA/Gaia, and the SDSS
Video (click to play)
This movie shows a computer simulation of a galaxy like the Milky Way. The movie fast-forwards through simulated time from 13 billion years ago to today. The main galaxy grows as many small galaxies merge with it. Heracles resembles one of the smaller galaxies that merged with the Milky Way early in the process.
Credits: Video built by Ted Mackereth based on the EAGLE simulations
Contacts
- Ricardo Schiavon, Liverpool John Moores University
R.P.Schiavon@ljmu.ac.uk
+44 (0)151 231 2945 - Daniel Horta-Darrington, Liverpool John Moores University
D.HortaDarrington@2018.ljmu.ac.uk
+44 (0)151 231 2923 - Karen Masters, SDSS Scientific Spokesperson, Haverford College
klmasters@haverford.edu, +1-610-795-6066
Twitter: @KarenLMasters / @SDSSurveys - Jordan Raddick, SDSS Public Information Officer, Johns Hopkins University, raddick@jhu.edu, +1-443-570-7105
Twitter: @raddick
About the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
Funding for the Sloan Digital Sky Survey IV has been provided by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science, and the Participating Institutions. SDSS acknowledges support and resources from the Center for High-Performance Computing at the University of Utah. The SDSS web site is www.sdss.org.
SDSS is managed by the Astrophysical Research Consortium for the Participating Institutions of the SDSS Collaboration including the Brazilian Participation Group, the Carnegie Institution for Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA), the Chilean Participation Group, the French Participation Group, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, The Johns Hopkins University, Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (IPMU) / University of Tokyo, the Korean Participation Group, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Leibniz Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP), Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie (MPIA Heidelberg), Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik (MPA Garching), Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), National Astronomical Observatories of China, New Mexico State University, New York University, University of Notre Dame, Observatório Nacional / MCTI, The Ohio State University, Pennsylvania State University, Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, United Kingdom Participation Group, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, University of Arizona, University of Colorado Boulder, University of Oxford, University of Portsmouth, University of Utah, University of Virginia, University of Washington, University of Wisconsin, Vanderbilt University, and Yale University.